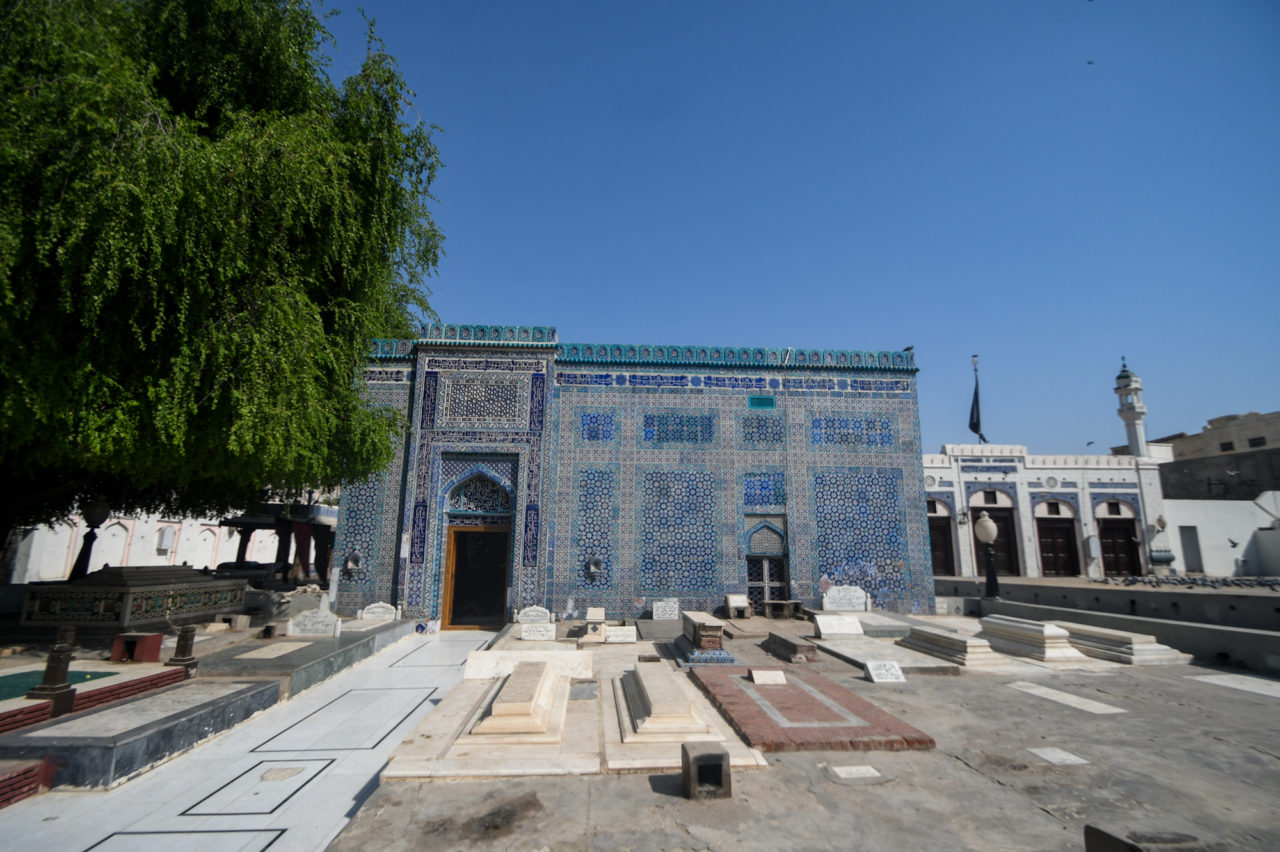
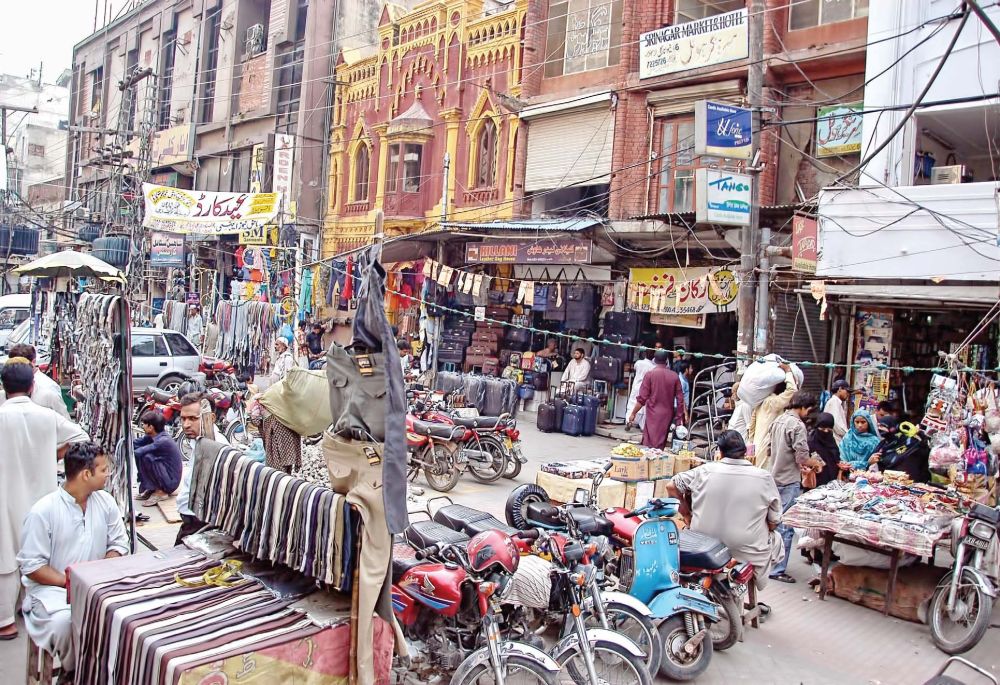
Hussain Agahi Bazaar, situated in the center of Multan, Pakistan, is a bustling and historically important market that plays a vital role in the city’s cultural and commercial life. Known for its rich cultural heritage and bustling atmosphere, this traditional bazaar offers a glimpse into the region’s past while serving as a hub for commerce and social interaction. The bazaar is a testament to Multan’s deep-rooted history, blending modern commerce with age-old traditions, making it an essential part of the city’s identity.
Historical Significance
Hussain Agahi Bazaar dates back centuries, with its origins tied to the ancient history of Multan. Historically, Multan has been a key center of trade, culture, and religion in South Asia, and Hussain Agahi Bazaar has always played an important role in these spheres. Over the years, it has seen various transformations, yet it retains its traditional charm and continues to be a popular destination for locals and tourists alike.
The bazaar is named after the revered figure of Hussain, a symbol of strength and righteousness in Islamic history. It is believed that this area has been a center for the exchange of goods and ideas, contributing to Multan’s reputation as a thriving city on the Silk Route.
Location and Layout
Situated in the historic city center of Multan, Hussain Agahi Bazaar is easily accessible from various parts of the city. It is strategically located near important landmarks such as the famous Multan Fort and the shrines of Sufi saints, which further enhances its cultural significance. The narrow, winding streets of the bazaar are lined with traditional shops selling a variety of products, from textiles to spices, jewelry to handicrafts.
The design of the bazaar blends traditional elements with modern features, creating a unique and dynamic atmosphere.While the bazaar has modern shops, the narrow alleys, historical buildings, and traditional signage retain the essence of Multan’s rich past. The vibrancy of the market, combined with the deep history embedded in every corner, gives visitors a unique experience.
Commerce and Shopping Experience
Hussain Agahi Bazaar is a commercial hub where local traders and artisans showcase their crafts. The market is famous for its wide range of goods, particularly Multani textiles such as the famous Multani suits, intricately designed pottery, handwoven fabrics, and embroidered shawls. Visitors can also find a variety of spices, dried fruits, traditional jewelry, and other items unique to the region.
The bazaar is known for its bargaining culture, where customers engage in friendly haggling to get the best prices for goods. This practice adds a touch of authenticity to the shopping experience, making it a lively and interactive environment.
Cultural Significance
Beyond its commercial activity, Hussain Agahi Bazaar holds immense cultural value. The marketplace has been a gathering point for the diverse communities of Multan for generations. It is here that social interactions and cultural exchanges take place daily, and the bazaar is often a place to observe traditional attire, cuisine, and local customs.
The nearby shrines and religious sites add a spiritual dimension to the bazaar, as many pilgrims visiting the city pass through the marketplace on their way to these sacred destinations. The presence of Sufi shrines in the vicinity has also contributed to the bazaar’s role in preserving the spiritual heritage of Multan, with many visitors seeking religious offerings, amulets, and prayers in the bazaar.
Food and Cuisine
Cuisine is another key highlight of Hussain Agahi Bazaar, drawing food enthusiasts from all over.. The streets are lined with small eateries and food stalls offering a variety of local delicacies. From the famous Multani Samosas and Chana Chaat to the rich flavors of local sweets like Multani Sweets and Khoya, the bazaar is a paradise for food lovers. The bustling atmosphere and aromatic smells from food stalls add to the charm of this traditional market, drawing both locals and tourists to sample the authentic flavors of the region.
The Modern Touch
While Hussain Agahi Bazaar is steeped in history, it has also evolved with the times. Modern businesses, including shops selling electronics, clothing, and contemporary accessories, have made their way into the bazaar, catering to the evolving tastes and demands of Multan’s urban population. However, despite these modern influences, the bazaar retains its traditional character, with the blend of old and new giving it a distinctive personality that appeals to both the younger generation and those with a deep appreciation for the past.
Conclusion
Hussain Agahi Bazaar in Multan is not just a shopping destination; it is a vibrant cultural hub that encapsulates the rich history and diverse traditions of the city. The bazaar offers visitors a unique blend of commerce, culture, and heritage, making it an essential part of any visit to Multan. Whether you’re interested in shopping for local crafts, enjoying the street food, or simply soaking in the bustling atmosphere, Hussain Agahi Bazaar promises an unforgettable experience that reflects the heart and soul of Multan.
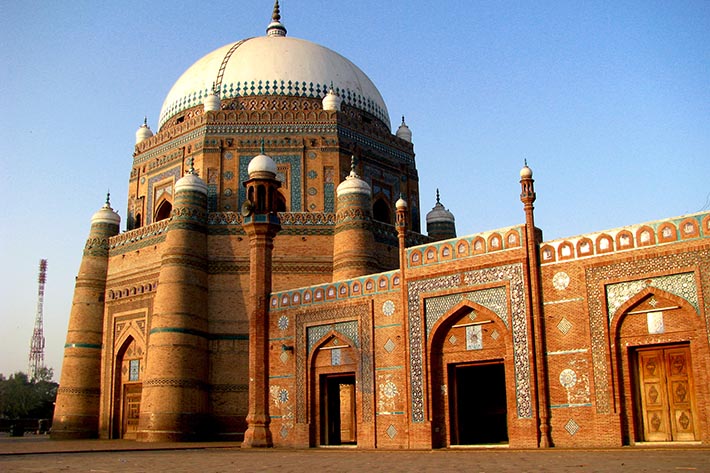
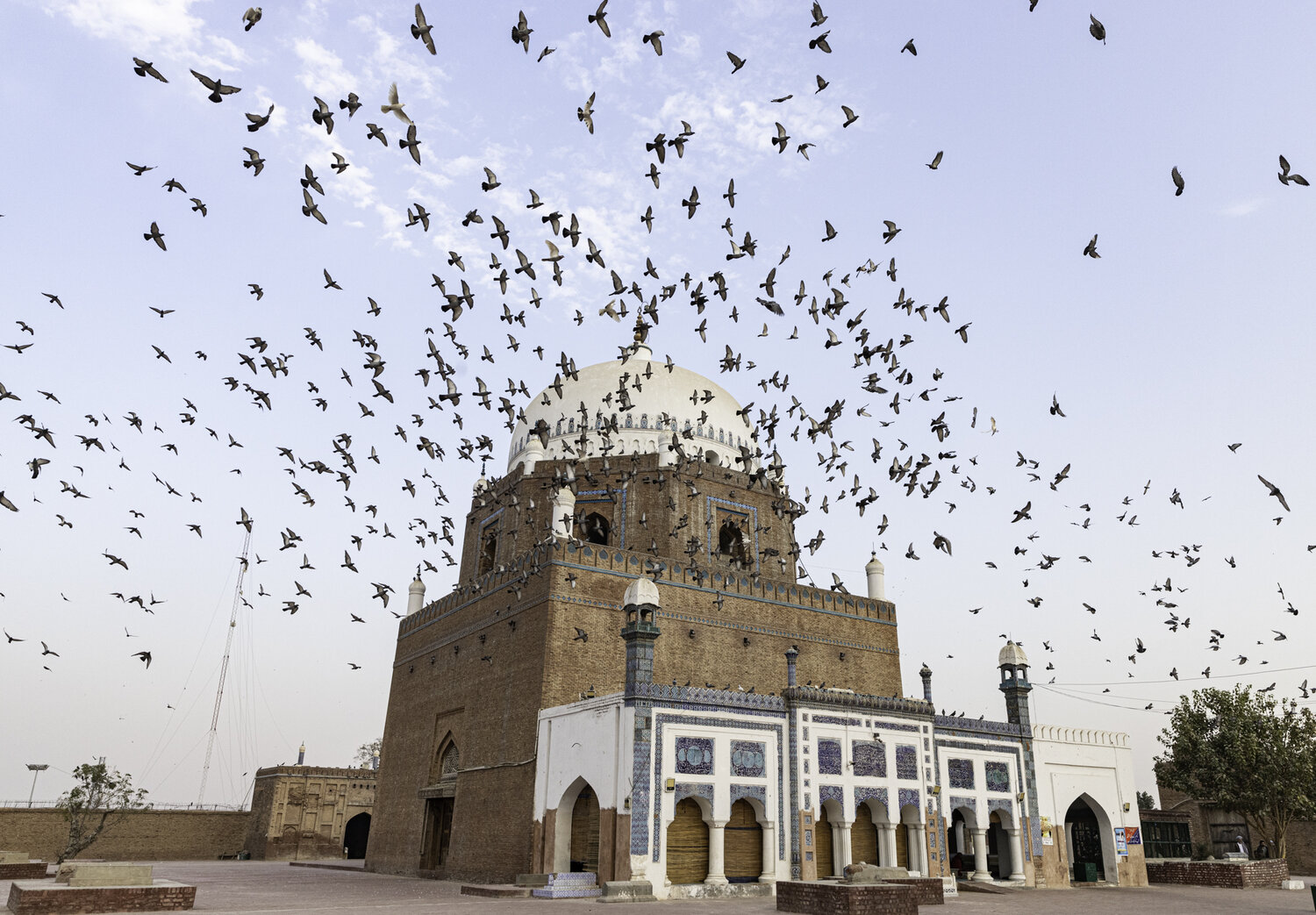




 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Peshawar7 years ago
Peshawar7 years ago