Introduction
The Tomb of Allama Iqbal is a revered site that pays homage to Dr. Muhammad Iqbal, the philosopher, poet, and visionary who is widely regarded as the spiritual father of Pakistan. Known as the “Poet of the East” and “Mufakkir-e-Pakistan” (Thinker of Pakistan), Iqbal’s literary and philosophical contributions inspired the Muslim community of South Asia. His tomb is not just a place of burial but a symbol of respect and admiration for his role in the intellectual and cultural awakening of the Muslim world.
Location
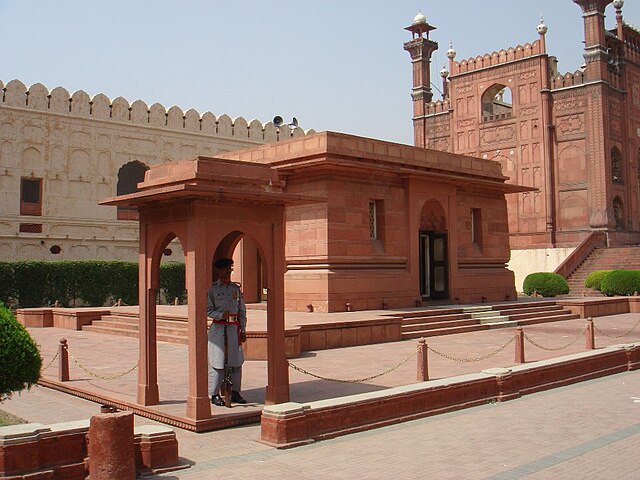
Although Allama Iqbal was born in Sialkot, Punjab, Pakistan, his tomb is located in Lahore, near the historic Badshahi Mosque and the Lahore Fort. This prominent location underscores the importance of his contributions to the nation. However, in Sialkot, Iqbal’s birthplace, a separate structure known as Iqbal Manzil serves as a museum and tribute to his early life.
Design and Architecture
The tomb of Allama Iqbal in Lahore is an exquisite blend of simplicity and grandeur, reflecting the humility and depth of Iqbal’s personality. The mausoleum was designed by Nawab Zain Yar Jang Bahadur, a renowned architect. It features elements of traditional Mughal and modern Islamic architecture, crafted from red sandstone brought from Jaipur, India, and white marble from Makrana.
The rectangular structure is surrounded by a low boundary wall and adorned with floral patterns. Inside, the cenotaph is made of white marble, inscribed with verses from the Quran and Iqbal’s poetry. The harmonious design of the tomb reflects Iqbal’s philosophy of balance between spiritual and material worlds.
Iqbal Manzil, Sialkot
In Sialkot, Iqbal Manzil serves as a counterpart to the Lahore tomb, preserving the memory of his birthplace and early life. Located in the heart of Sialkot’s old city, this ancestral house has been converted into a museum. It houses a collection of Iqbal’s personal belongings, rare manuscripts, photographs, and letters, giving visitors an intimate glimpse into his formative years.
Significance
The tomb of Allama Iqbal is more than just a grave; it is a beacon of inspiration for people from all walks of life. Visitors from across Pakistan and abroad come to pay their respects, draw inspiration from his teachings, and reflect on his vision of a prosperous, independent Muslim state. His poetry continues to resonate with themes of self-realization, unity, and resilience, making the mausoleum a sacred site for Pakistanis.
Cultural and Historical Context
Both the tomb in Lahore and Iqbal Manzil in Sialkot highlight the enduring legacy of Allama Iqbal. His role in shaping the intellectual foundation of Pakistan ensures that these sites are not only places of remembrance but also venues for cultural and academic engagement. Events such as Iqbal Day, observed on November 9th, see these locations filled with admirers and scholars, emphasizing their cultural significance.
Visitor Experience
The serene atmosphere of the Lahore tomb is complemented by the nearby historical landmarks, making it a must-visit for tourists and history enthusiasts. In contrast, the Sialkot museum offers a more personal experience, connecting visitors to the poet’s roots. Both sites offer an educational journey through Iqbal’s life and his contributions to society.
Conclusion
The Tomb of Allama Iqbal and the Iqbal Manzil in Sialkot stand as enduring tributes to one of South Asia’s greatest minds. Together, they encapsulate the essence of Iqbal’s life, from his humble beginnings in Sialkot to his monumental influence on the creation of Pakistan. These sites remain vital for preserving his legacy and continuing his mission of intellectual and spiritual awakening.




 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Uncategorized7 years ago
Uncategorized7 years ago
 Peshawar7 years ago
Peshawar7 years ago